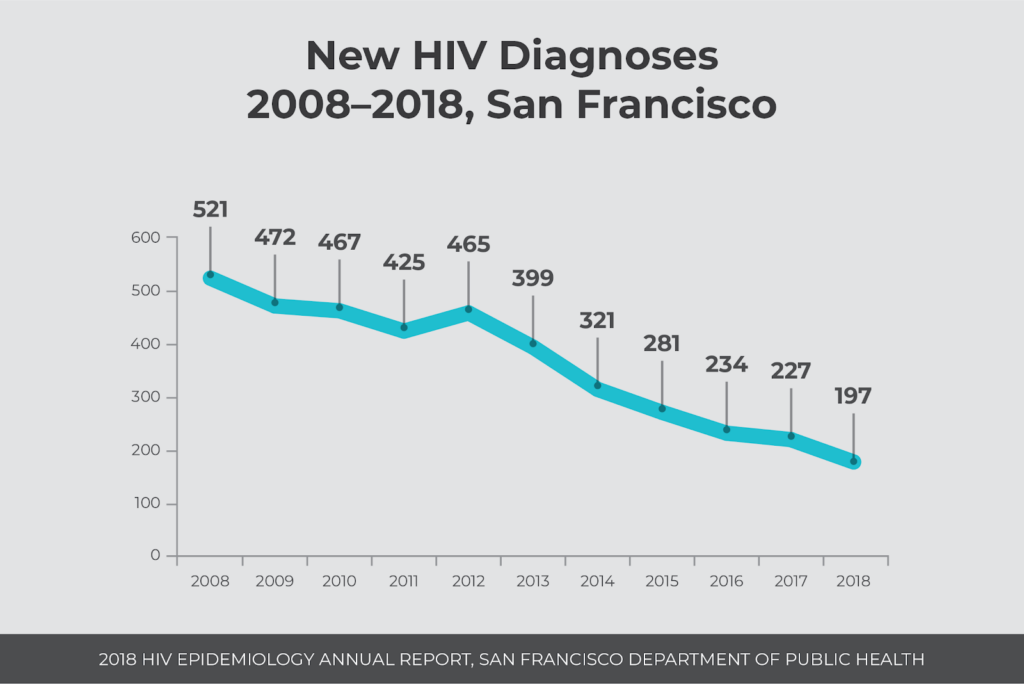
Yearly HIV infections in San Francisco drop to 197

Every year, the San Francisco Department of Public Health (SFDPH) publishes a comprehensive report on HIV incidence and prevalence in the city, showing HIV trends to guide the public health response. Continuing a downward trend since the peak of the HIV epidemic in the 1990s, the most recent report with 2018 data shares a historic milestone reached by the city: Fewer than 200 HIV diagnoses occurred in San Francisco.
A total of 197 people were diagnosed with HIV last year in San Francisco. This is a 13% decline from 227 diagnoses made in 2017, and a 62% decline from 523 infections ten years ago in 2008. The peak number of HIV diagnoses in San Francisco occurred in 1992 with 2,327 diagnoses.
Most people (94%) living with HIV are aware of their status, and 91% of people newly diagnosed with HIV in 2018 entered care within one month. It is estimated that 74% of people with a last known address in San Francisco who are living with HIV were virally suppressed in 2017.
“I am really delighted that we in San Francisco, since the 1980s, have been at the forefront of pushing for innovative ways to change policies, new sciences and technologies to help us get to this milestone,” said Mayor London Breed at a press conference at Zuckerberg San Francisco General’s Ward 86. “This shows that when we work together with the community, with our policy makers, with our public health experts, and our nonprofits we can make a difference and save people’s lives.”
“We are pleased, but not satisfied,” said Diane Havlir, MD, who spoke on behalf of the Getting to Zero consortium. “We’re not satisfied because we had nearly 200 new diagnoses of HIV in our city—and it’s a preventable disease.”
Differences by Race and Ethnicity, Housing Status and for People who Inject Drugs
People of color, people experiencing homelessness and people who inject drugs continue to experience higher diagnosis rates, lower viral suppression rates and lower survival rates.
People of color are disproportionately affected by HIV
African American and Latinx men had the highest diagnosis rates (145 and 89 per 100,000), and rates increased from previous years. Diagnosis rates for white men have declined steadily since 2012. Among women, African Americans had a much higher diagnosis rate (35 per 100,000) than women of other races.
Overall, 74% of people living with HIV in San Francisco were virally suppressed, while viral suppression rates were lower for African Americans (68%), trans women (68%), women (66%), people who use injection drugs (65%), men who have sex with men who inject drugs (68%) and trans women who inject drugs (64%).
“San Francisco continues to make unprecedented progress towards ending the HIV epidemic,” said Joe Hollendoner, CEO of San Francisco AIDS Foundation. “However, we continue to see racial disparities related to HIV health outcomes. To end HIV transmission and AIDS-related deaths, the public health system needs to address the systemic racism that is inhibiting our progress.”
“We have to double down on these gaps that we’re seeing,” said Havlir. “We need to listen, and we need to deploy new innovative approaches with tools that have. With PrEP. And with upcoming tools like long-acting injectable [HIV] therapies which could make it a lot easier for some of our populations.”
Homelessness compounds HIV risk and severity of health outcomes
As the number of new HIV diagnoses shrinks year after year in San Francisco, and the number of people experiencing homelessness grows, a higher proportion of HIV diagnoses are occurring among people without access to medical care, social support and prevention resources—in particular people without housing.
In 2018, 20% (40) of new HIV diagnoses were among people without housing compared to 10% (29) in 2015. There were 8,011 people experiencing homelessness in San Francisco in January 2019, according to the 2019 San Francisco Homeless Point-in-Time Count and Survey, a 14% increase since 2013.
People without housing are also much less likely to be virally suppressed. Only 33% of people experiencing homelessness were virally suppressed, compared to 74% of people overall.
“We know that many elements that are key to success, for people living with HIV, are challenging if you don’t have a place to live,” said Monica Ghandi, MD, MPH, medical director of the SFGH HIV clinic. “That would be like making and keeping appointments. Where you store your medications, and where you keep them safe. Maintaining safe sex, and healthy eating. All of these barriers to taking your medications every day are amplified 100-fold if you don’t have a home.”
“Our focus on disparities really has to focus on ensuring that we reach people where they are,” said Hyman Scott, MD, MPH from Bridge HIV at SFDPH. “There are no ‘hard to reach’ populations—there are just ‘hard to deliver’ services. We need to re-think the way we approach some of these services that we deliver.”
HIV and people who inject drugs
People who inject drugs account for 25% of new HIV diagnoses, (10% are men who have sex with men who inject drugs; 1% are trans women who inject drugs; 14% are other people who inject drugs), a proportion which has risen over the years.
In addition to accounting for a higher proportion of HIV diagnoses, injection drug use is associated with worse health outcomes: People who inject drugs are less likely to be virally suppressed and have lower three-year survival rates after an AIDS diagnosis.
The percentage of people who are diagnosed with HIV who inject drugs is rising steadily every year, while reductions are seen in other populations including men who have sex with men.
“San Francisco has a robust syringe access program, which has kept HIV transmission rates low among people who inject drugs, but it’s not sufficient to eliminate HIV transmission among people who inject,” said Laura Thomas, director of harm reduction policy at San Francisco AIDS Foundation. “Housing instability and displacement make it challenging for people who use substances to always do so safely. That’s why it’s so important for us to establish safe injection sites in our city.”
“Unless we invest in expanding low barrier substance use and mental health counseling services like those offered at our Harm Reduction Center and at the Stonewall Project, I worry that increased HIV infection trends like those we’re seeing with people who inject drugs will continue,” said Mike Discepola, MA, senior director of behavioral health services and the Stonewall Project at San Francisco AIDS Foundation. “We will not get to zero new infections in San Francisco unless we focus services on our most vulnerable populations. This includes those who inject and use drugs, are experiencing homelessness or have untreated mental health concerns.”
An Aging HIV Population
With nearly 16,000 people living with HIV in San Francisco, two-thirds (10,691 people) are age 50 and older.
“We know that this is the generation that didn’t plan to live,” said Vince Crisostomo, manager of the Elizabeth Taylor 50-Plus Network at San Francisco AIDS Foundation. “They didn’t plan financially, they didn’t set up 401Ks. But, they did live. And service providers need to be thinking about how to adjust services to meet the needs of these long-term survivors. How can we provide culturally competent services for people of older age who are living with HIV?”
“To end the epidemic we cannot leave anyone behind,” said Hollendoner. “We must achieve this ambitious goal together and prove to the world that it can be done.”
Guided by a new 5-year strategic plan, San Francisco AIDS Foundation charts a course for improving the sexual health outcomes of people of color and other priority communities, establishing safe injection sites, creating a comprehensive network of health and wellness services for people over age 50 who are living with HIV, and living our values of racial justice.











